Example 1 (one codon)
Input: CCU
Output: Pro
Output: Pro
You might want to solve DNA transcription first to learn how to transcribe DNA into RNA.
Once DNA has been transcribed into RNA, the RNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids that can then fold into a protein. The genetic code describes
how RNA is translated into amino acids. Translation happens one codon at a time where each codon consists of three nucleotides, such as GUA or
ACG, and gets translated into one amino acid.
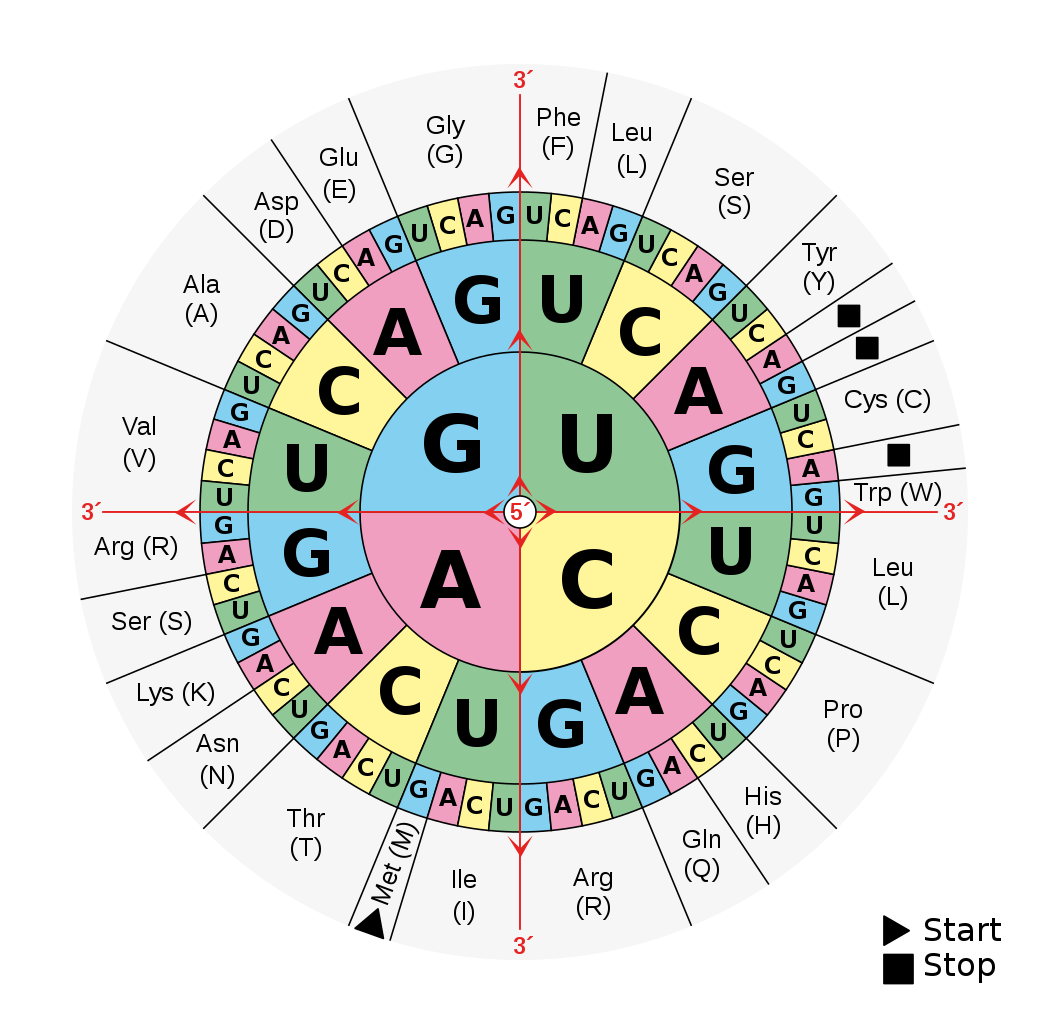
GCA
codon translate to the Ala (Alanine) amino acid.
Write some code to translate an RNA sequence into a sequence of amino acids. If you encounter a stop codon, then stop translation and return the amino acid sequence up until the stop codon (but not including it).
Input: An RNA sequence.
Output: A sequence of amino acids.
| Difficulty | Timesink | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Function | amino_acid_sequence(rna) | ||
You must be logged in to view your submissions.
Let us know what you think about this problem! Was it too hard? Difficult to understand? Also feel free to discuss the problem, ask questions, and post cool stuff on Discourse. You should be able see a discussion thread below. Would be nice if you don't post solutions in there but if you do then please organize and document your code well so others can learn from it.